In 2025 so far, we’ve seen 15,494 new CVEs published. Consider, however, that exposure management goes beyond just CVEs. It also covers security weaknesses like misconfigurations, design flaws, and subpar or missing security controls. Note that this is not just in your own modern systems, but also in your software supply chain and legacy components. Can you imagine the magnitude of the mission that exposure management is trying to accomplish?
The unprecedented complexity and interconnectedness of modern digital environments make all-encompassing exposure management necessary. Yet the sheer scale of security weaknesses often outpaces security teams’ capacity to deal with threat exposure effectively. The way exposure management is predominantly done simply doesn’t cut it.
To fortify your defenses, you must move beyond prioritizing security weaknesses and relying on unduly prolonged remediation cycles. The way we see it, autonomous exposure mitigation is the most viable proactive approach for dealing with the existing and emerging threat landscape.
Autonomous exposure mitigation closes the loop by resolving security risks off the bat, transforming exposure management from virtually a diagnostic exercise into an effective remediation process. How precisely does it do that? Read on to discover.
What Is Exposure Management?
A strong security posture must be predicated on a strong exposure management program. But first, what does exposure management even entail? And how strong is it in its predominant form?
Defining Exposure Management
Managing exposure means identifying, evaluating, and addressing the security weaknesses that can expose your digital assets—systems, applications, devices, or data—to malicious actors.
Exposure management incorporates threat intelligence to help you better grasp the current threat landscape. You learn about known exploited vulnerabilities (KEVs) and threat actors’ tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). That leads to a comprehensive and continuous understanding of your overall attack surface, which allows you to put security weaknesses in perspective.
More precisely, exposure management enables you to single out the threats that pose the most severe risk to your unique environment, prioritize your security efforts accordingly, and shut down first those attack entry points that are most likely to be exploited or would cause the greatest impact if compromised.
The Limitations of Standard Exposure Management
Everything we said implies that exposure management is invaluable. Still, with all the value it has, you must not lose sight of its drawbacks.
For starters, in terms of concrete security technology solutions—exposure management security tools and platforms—exposure management doesn’t always include remediation.
Many exposure management platforms excel at discovery, vulnerability scanning, asset inventory, and risk scoring, providing all the data and insights necessary for remediation. However, they don’t directly perform the remediation tasks themselves.
An exposure management solution might integrate with other security tools (like patch management systems or configuration management tools) to facilitate remediation workflows, but the actual execution of the fix happens in those separate systems.
In that sense, exposure management acts as an important intelligence-gathering and prioritization engine that informs subsequent security operations and remediation efforts but does not by itself lead to remediation.
On the other hand, exposure management as a discipline or program absolutely includes remediation as a vital stage. A comprehensive exposure management strategy is incomplete without the actions taken to fix identified weaknesses.
Nonetheless, the way it’s typically done—with remediation in the form of patching coming at the end of long identification and prioritization phases—takes too much time and resources. The gravest problem with this approach is that while you’re identifying and prioritizing, your environment remains open to new threats and cyberattacks. And let’s not forget that remediation (as patching) itself is an overly long and resource-intensive process, as well.
What this means is that exposure management calls for a different approach. An approach that’s more suitable for dealing with the colossal complexity and supersonic speed of changes in the contemporary threat landscape.
What Is Autonomous Exposure Mitigation?
We saw what exposure management is and where it falls short. Now, it’s time to explore autonomous exposure mitigation and see why it is the better approach.

Definition and Overview
Autonomous exposure mitigation is a leap forward in proactive security, fully focused on immediate threat reduction. Unlike tools that primarily identify and assess vulnerabilities, an autonomous exposure mitigation solution neutralizes risks right after deployment and continuously prevents threats from causing full-fledged incidents in real time.
Autonomous exposure mitigation typically relies on predefined trust policies, a verified baseline, and an AI or ML engine to ensure your environment stays protected regardless of whether you face CVEs, zero-day vulnerabilities, or some other type of exposure.
Its immediate actions can range from applying virtual patching to systems and implementing compensating controls in out-of-date software to blocking malicious, suspicious, or, for that matter, any anomalous behavior.
By directly intervening to eliminate or contain threats without manual delays, autonomous exposure mitigation reduces the window of opportunity for attackers, aiming at zero-dwell time.
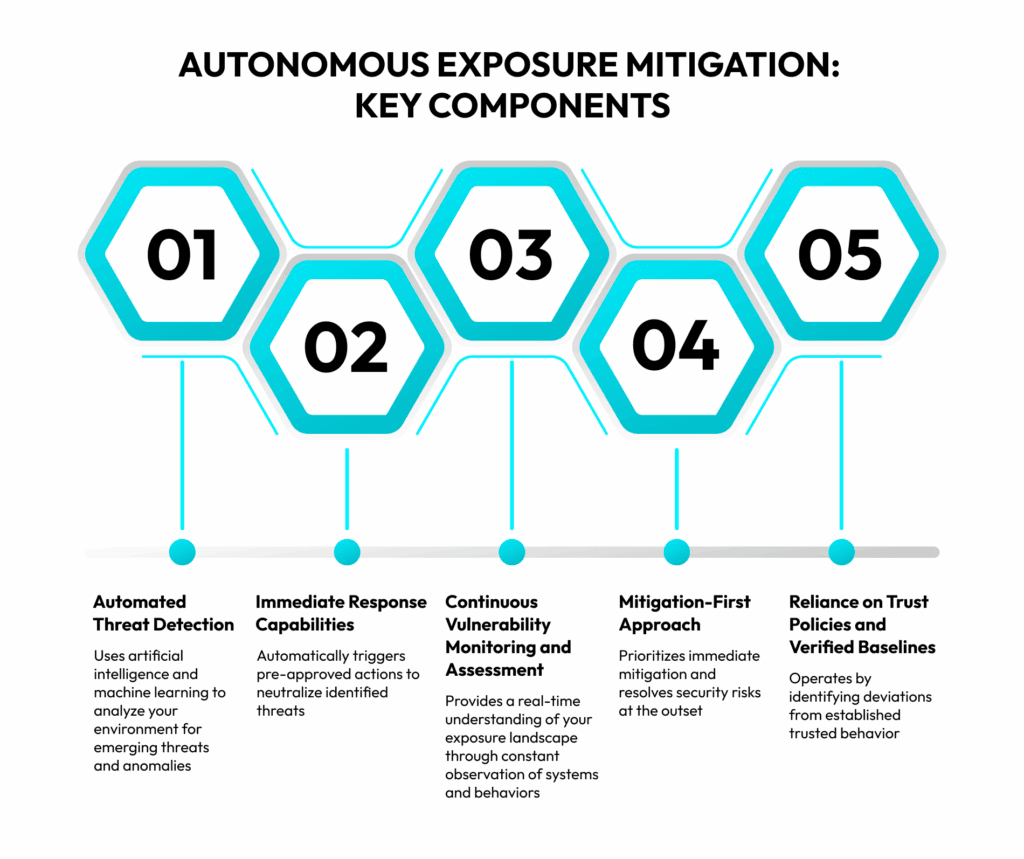
The Key Components of Autonomous Exposure Mitigation
Autonomous exposure mitigation relies on a few key elements working in unison to deliver rapid and effective threat reduction.
Automated Threat Detection
At the core of autonomous exposure mitigation lies sophisticated automated threat detection. This capability depends on the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning to continuously track your digital environment for the emergence of new vulnerabilities, indicators of compromise, or evolving attack patterns.
The advantage of AI and ML engines is that they can analyze petabytes of security data in a short time, spot subtle anomalies that might indicate malicious activity, and proactively flag potential threats that traditional rule-based systems might miss.
Instant Response Capabilities
Another defining characteristic of autonomous exposure mitigation is its ability to act swiftly and decisively to neutralize threats without human intervention.
Once a threat or critical vulnerability is identified and validated based on predefined security policies or an established baseline, the autonomous system can trigger pre-approved mitigation, that is, remediation actions. This near-instantaneous response can substantially lower the probability of attackers moving laterally and causing severe damage to your environment.
Continuous Vulnerability Monitoring and Assessment
Proactive security requires incessant vigilance against known but also unknown weaknesses.
For this reason, autonomous exposure mitigation incorporates continuous vulnerability assessment that goes far beyond periodic scanning. It includes constant evaluation of the state of networks, systems, applications, and cloud environments to identify suspicious or plainly malicious changes. That, in turn, presupposes around-the-clock tracking and observation of all the code and processes within your environment.
Continuous vulnerability monitoring and assessment ensures an up-to-date understanding of your exposure landscape, which makes it possible to promptly address novel CVEs or missed exposures before threat actors get the chance to exploit them. And that’s not a small feat, considering that time-to-exploit for CVEs has recently dropped drastically, with a large percentage of vulnerabilities exploited within the first 24 hours of disclosure.
Why Exposure Management Alone Isn’t Enough
Spoiler alert: Exposure management alone doesn’t cut it, because without timely remediation, organizations are left exposed to all kinds of external and internal threats.
The Evolving Nature of Cyber Threats
The threat landscape is evolving at a full tilt, and cyberattacks are escalating in sophistication and speed. Just think Salt Typhoon and Volt Typhoon.
Threat actors use increasingly advanced techniques like AI-powered social engineering, zero-day exploits, and ransomware with complex evasion capabilities to execute subtle attacks at a velocity that, more often than not, outpaces human response times by far.
This unenviable state is why standard exposure management, which primarily focuses on identifying and prioritizing security weaknesses, is no longer sufficient on its own. Indeed, understanding your exposures is necessary, but the speed and complexity of modern attacks demand proactive, automated, and prompt protection.
To effectively close the gap that manual remediation struggles to bridge, you must be able to neutralize cyberattacks as they happen without solely depending on the vigilant eye of security professionals. That is especially true given the vast cybersecurity workforce deficit.
Reactive vs. Proactive Approaches
Exposure management, while aiming for proactivity, often requires manual intervention for remediation, making its impact on reducing the attack surface somewhat delayed. In contrast, autonomous exposure mitigation embodies a much more proactive stance—it addresses security risks immediately and in real time. You can’t go more proactive than that.
By adopting a mitigation-first approach and automating mitigation, you’re bound to minimize your attack surface. It’s the simplest way to bolster your defenses against weaknesses that hackers can otherwise exploit before manual remediation takes place.
How Autonomous Exposure Mitigation Closes the Loop
Autonomous exposure mitigation emerges as a powerful paradigm, automating threat detection and delivering immediate remediation to essentially create a self-healing security posture.
Automated Threat Detection and Remediation
An autonomous exposure mitigation solution continuously monitors your environment for indicators of compromise, using AI and machine learning to detect and assess emerging threats and known vulnerabilities as fast as possible. When it spots a security risk and confirms it’s there, the solution triggers an immediate, pre-defined remediation action without human intervention, closing the gap between detection and response.
For instance, in the face of a newly discovered software flaw, an autonomous solution can apply virtual patches—temporary fixes deployed at the network or host level that block exploit attempts without requiring immediate code changes. This action neutralizes the threat without downtime and the usual complex patching processes, removing the dangers that long patching cycles entail.
The Benefits of Autonomous Exposure Mitigation
By now, the benefits of autonomous exposure mitigation have become pretty much clear. However, to reiterate the main points in a more systematized fashion, autonomous exposure mitigation leads to:
- Faster threat response: An autonomous exposure mitigation solution cuts the time between the detection of an actual threat and its neutralization to milliseconds, allowing you to achieve zero-dwell time.
- Higher efficiency: Automating the typically time-consuming remediation processes frees up precious resources, allowing security teams to turn their full attention to more strategic tasks and proactive threat hunting, ultimately improving security operations efficiency.
- More consistent security posture: The continuous nature of autonomous exposure mitigation provides strong and adaptive protection. By constantly monitoring for new threats and automatically addressing weaknesses, autonomous exposure mitigation enables you to remain secure even as the threat landscape evolves and new attack vectors emerge.
How to Implement Autonomous Exposure Mitigation
Okay, we’ve discussed autonomous exposure mitigation and looked at its benefits. Now, its time to learn how to implement it practically.
Step 1: Integrate AI and Machine Learning for Threat Detection
Incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning for advanced threat detection involves deploying an AI-powered security platform purpose-built for automated exposure mitigation. It must be able to continuously analyze data from across your IT environment to detect deviations from the baseline system and software behavior that points to threats.
An AI or ML engine is critical in identifying subtle anomalies, enabling an autonomous threat response, and enforcing only trusted software to run. It learns from different parts of your systems to proactively detect known and novel threats with a much greater speed and accuracy than traditional rule-based systems.
Step 2: Adopt a Mitigation-First Approach and Automate Remediation
The immediate neutralization of threats is what autonomous exposure mitigation is all about. Its whole point is to begin with the most important aspect of managing exposure, that is, remediation, and leave as little room as possible for attackers to fulfill their objectives.
When you use a security solution that can instantly block known and zero-day threats without patching, you can achieve true zero mean time to remediate. This approach can involve locking down servers, software, and identity at runtime, and ensuring continuous system integrity.
It’s the only plausible way to eliminate the risks associated with lengthy patching cycles and potential downtime.
Step 3: Implement Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
Implementing continuous monitoring and adjustment within an autonomous exposure mitigation strategy means leveraging a security solution that analyzes application behavior and deviations from the known baseline 24/7.
In that sense, a platform with an incorporated zero-trust approach can do wonders. Inherent zero-trust principles allow it to validate the trustworthiness of the executed code and processes repeatedly and autonomously. So when it detects unauthorized changes or probable exploitation, it automatically prevents a full-fledged cyberattack, as it would include deviation from the trusted behavior.
As the autonomous exposure mitigation solution monitors your environment, it can respond to new, unknown threats without the need for manual rule updates or human intervention. Its ability to learn from previous experience and subordinate everything to the verified normal system and application behavior ensures that it remains adaptable and effective over time.
Conclusion
As the cyber threat landscape intensifies in speed and complexity, standard exposure management alone falls short.
Autonomous exposure mitigation represents a crucial step forward. It automates threat detection and applies real-time, that is, immediate remediation, delivering a more resilient security posture that can withstand the towering waves of old and new, known and unknown security threats.
Want to see autonomous exposure mitigation in action? Book a demo.
FAQ Section
What is autonomous exposure mitigation?
Autonomous exposure mitigation is a security approach that uses automation to continuously protect your environment by applying mitigation actions right off the bat. Instead of hinging on patching and postponing remediation until after the identification and prioritization stages, it addresses your critical vulnerabilities and exposures at the very beginning, avoiding the risks of untimely remediation.
How is autonomous mitigation different from standard exposure management?
Autonomous mitigation differs from standard exposure management in two main ways:
- It emphasizes mitigation instead of prioritization and patching.
- It automatically takes action to neutralize detected threats in real time, rather than relying on manual intervention for remediation.
How can I implement autonomous exposure mitigation in my business?
The simplest and easiest way is to embrace a security solution that:
- Adopts a mitigation-first approach
- Incorporates zero-trust principles
- Offers continuous asset discovery
- Relies on AI or ML engines/agents
- Recognizes even subtle changes in your environment
- Prevents cyberattacks in milliseconds—before they become breaches or full-blown security incidents



