Virsec's Latest Security Platform Release: Application Visibility, Automated Allowlisting, and Operational Efficiencies
A Zero Trust Architecture provides the security framework for users, assets, and resources within an enterprise. The focus on users, or human-to-application interconnection, has led to innovations in identity and access management but has also introduced a dependency that breaks when the interconnection is application-to-application. The reliance on identity management and network-based controls may impede many attackers but does little to prevent modern Remote Code Execution (RCE), fileless, and memory-based attacks, offering enough attack surface to establish a beachhead for further malicious actions and lateral movement. This is specifically impactful when the cyberattack aims for internet-facing servers, as the higher number of users, data, and permissions for lateral attacks make it more profitable and appealing.
Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report
The Speed of Cyber Attacks
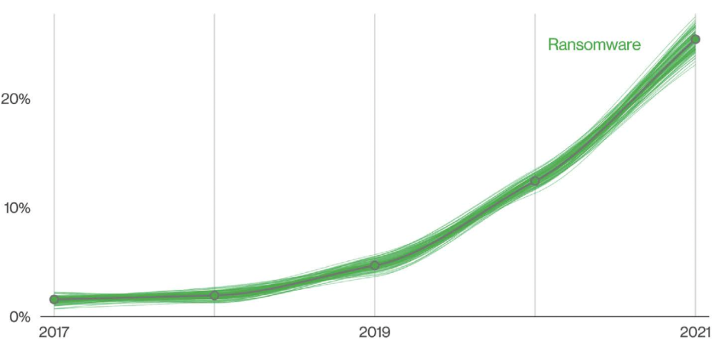
The speed at which ransomware attacks infiltrate, weaponize, and exploit vulnerabilities is increasing, making continuous security to stop zero-day attacks more urgent to protect critical data and systems. As nation-states and cyber criminals game the system and jump on known CVE and CWE vulnerabilities to scan for targets, closing the attack surface in time to prevent being exploited becomes a high priority.

Time to Exploit Ransomware
As shown above, current ransomware attacks can detonate an exploit within half a second. With few mitigating security controls to stop malware or ransomware exploits against application workloads, IT organizations are often left with reactive responses focusing on containing, triaging, and remediating after the cyber-attack detonates.
As the cyber-attack unfolds, time becomes a major constraint. In IBM’s Ransomware, time-to-encrypt decreased by 94%. Combined with the 0.5 seconds it takes to exploit malware, the problem becomes more acute and urgent today than ever before.
Defense in Depth Security Strategy
Zero Trust Architectures lean heavily on the user's identity and network-based perimeter controls to segment and contain threats. But once those two elements are compromised, most organizations are left with no ‘plan B.’ With Virsec, additional mitigating security controls provide zero trust protection for application and host workloads without dependencies on identity or network access. The core tenant of this defense-in-depth strategy is that data must be protected, applications must continue to operate for the health of the business, and workloads must be protected regardless of patch status.
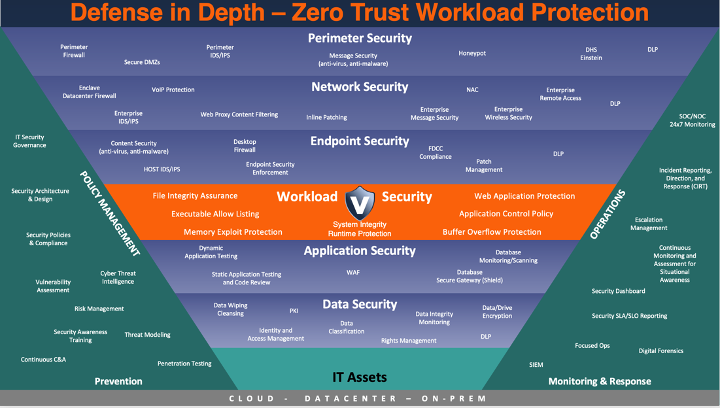
Defense in Depth – Extending Zero Trust to Application and Host Workloads
In many Zero Trust Architectures, the definition of ‘endpoint’ encompasses everything, from mobile devices to laptops, servers, and supercomputers. Virsec’s security controls focus on protecting server workloads, as servers have distinctive characteristics that require a different security posture than mobile devices and laptops.
To start with, servers typically do not move locations or geo-sites; in fact, highly secure servers may be segmented and air-gapped away from any internet connection at all. Adding to the differences would include application deployments – typically, server applications are tested, authorized, and managed. Generally, ‘Bring Your Own Application’ processes are not condoned, and permissions to add, change or delete are restricted to Administrators or Super Administrators. But most importantly, servers are a many-to-one environment that holds business-critical data, making it the number one target for cybercriminals and nation-states who leverage Remote Code Execution (RCE), fileless, and ransomware zero-day attacks for their exploits. Keeping the castle safe is key for business continuity and maintaining trust with customers and suppliers.
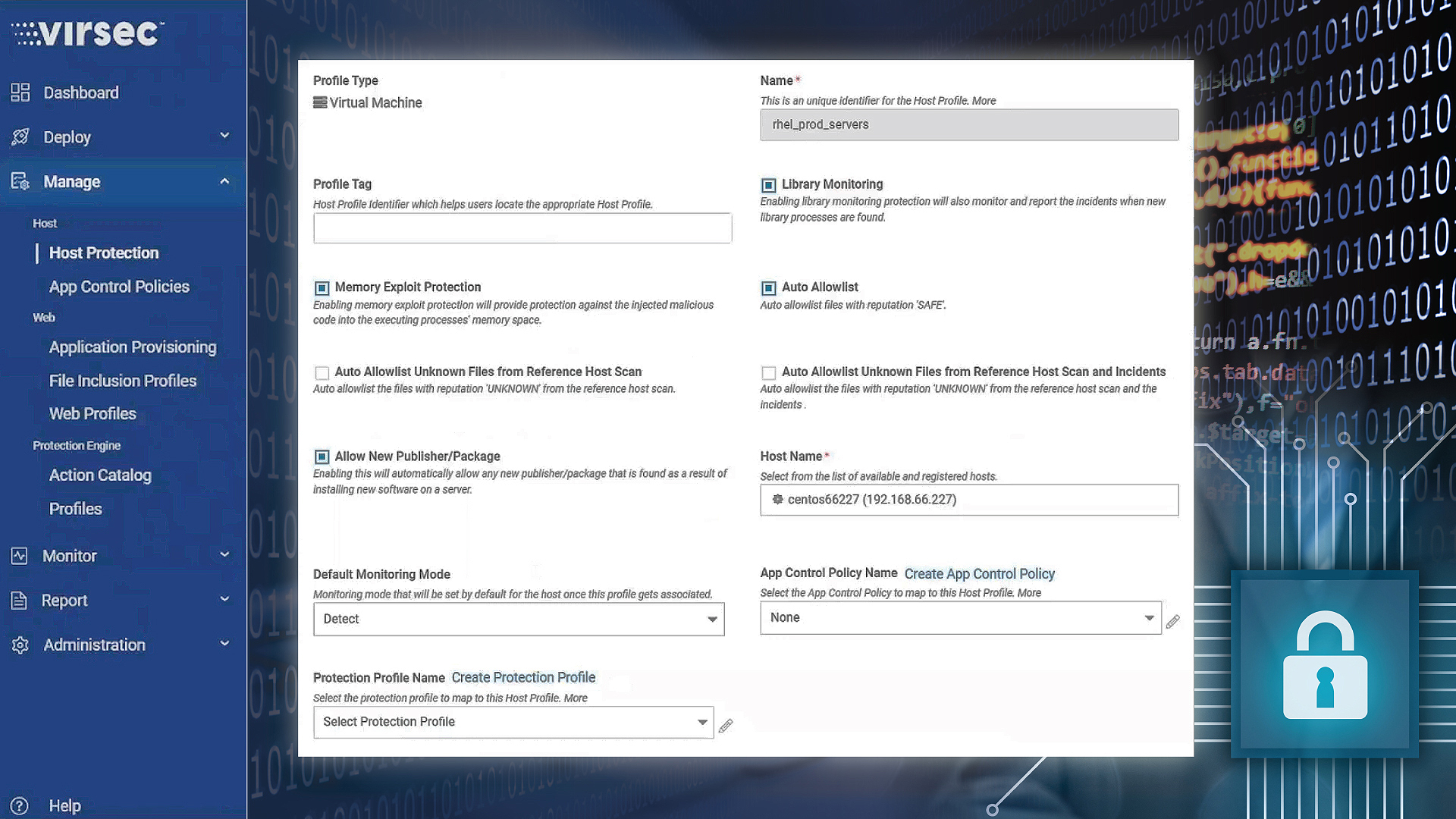
Virsec Security Platform (VSP) Release 2.7
In this latest release, Virsec expands Zero-Trust protection principles to application workloads with new capabilities for continuous protection, including extensions to allow listing automation, application workload visibility, operational efficiencies, and ease of use.
Allowlisting Automation
Application Control is fundamental to extending zero trust protection to application workloads as they allow granular control over the dynamic execution of scripts, processes, files, and libraries at runtime. The allowlist defines the ingredients (aka “software bill of materials”) authorized to run by the workload, whereas Application Control Policies (ACP) define how those components should collaborate in the runtime.
Virsec’s approach to allowlisting strikes the right balance between granular control, ease of onboarding, and day-2 operation. VSP 2.7 enables automation of granular allowlisting by leveraging meta-data that is captured from digital certificates and packages. Customers now have the option to to-allow new publishers and packages for server workloads, drastically simplifying without service interruptions. This added automation eliminates hours of manual effort in managing allowlists, and stops false positives from new ‘known good’ files appearing at runtime.
See Virsec's Automated Allowlisting Packages & Publishers ![]()
Application Workload Visibility
Many IT organizations are divided between application and infrastructure teams, with security overlapping both. The boundary of responsibilities often results in shadow IT running on workloads that operate without appropriate application security.
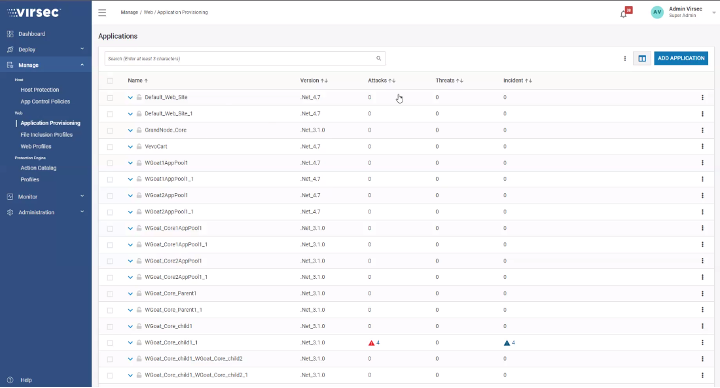
Virsec Application Workload Discovery
In VSP 2.7, the Virsec probe automatically scans and discovers web applications across Linux and Windows VMs to provide application visibility across public cloud instances, private cloud instances, data centers, and hybrid environments. It automatically scans for application instances after installation to discover the web applications hosted across the environment and verify their compatibility with the Virsec web protection technology. Now Virsec Security Platform (VSP) customers have visibility into the discovered applications name, version, and IP address, and with a single click, they can enable the appropriate protections for a given web application instance.
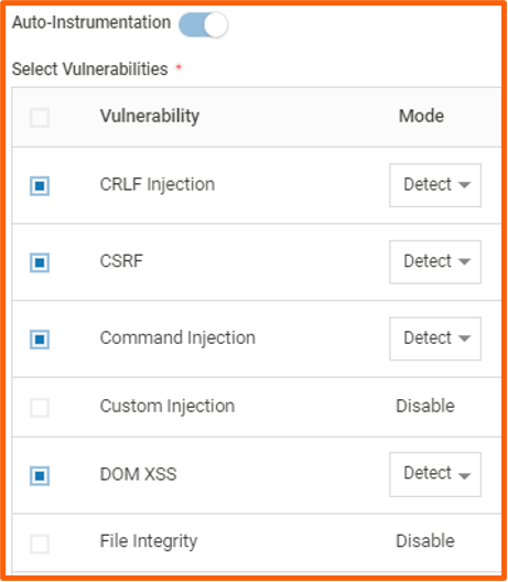
Protection Options for Auto-discovered Applications
See Virsec's Application Auto-Discovery ![]()
Granular Event Descriptions for Application Incidents
Application Control Policies (ACP) related incidents are now reported as a separate category and with additional insights and visibility for faster triage and analysis. The new class of events is presented in the central management system (CMS) under “App Control Violation” with descriptive information for additional visibility into dynamic execution of allowed applications that typically result in living-off-the-land attacks.
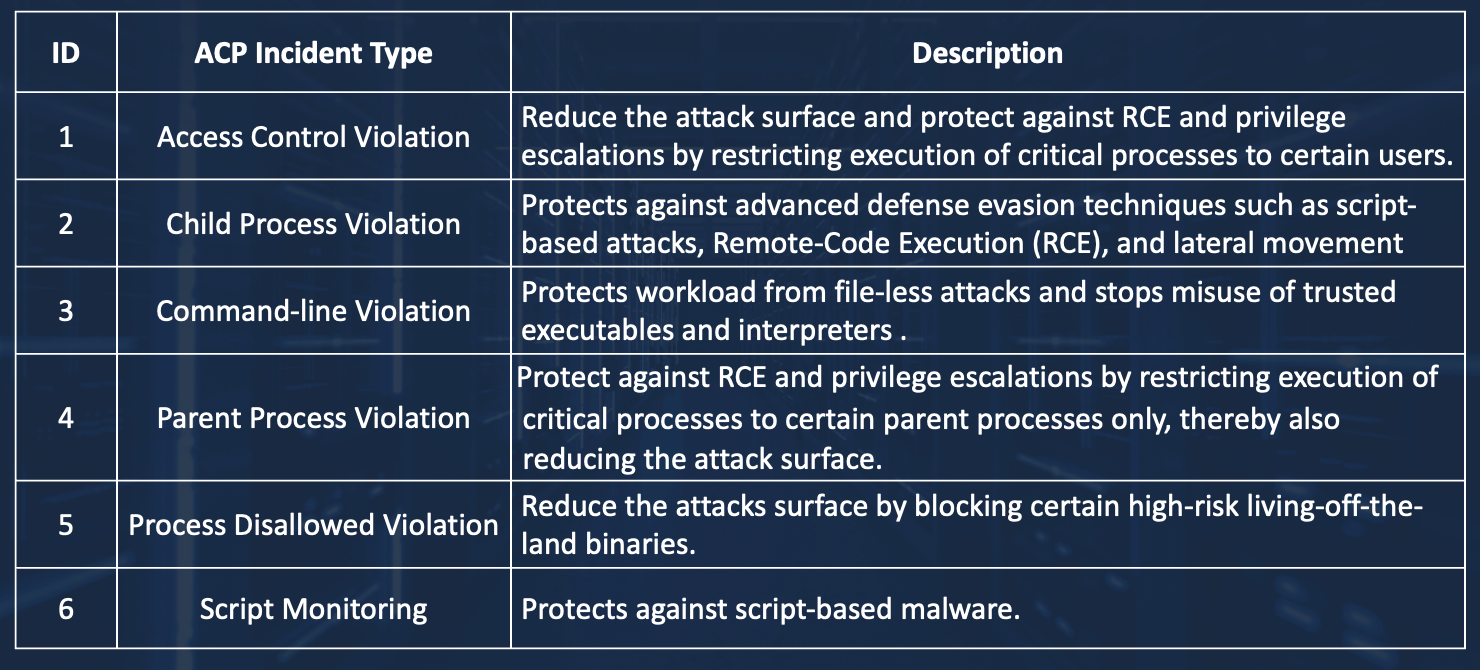
Virsec Application Control Policies (ACP) Incident Types
Visibility into the cause of a security incident provides Incident Response teams valuable insights into a violation of authorized runtime execution that may lead to infiltration or exploits of a vulnerability by bad actors. The Virsec Security Platform (VSP) presents six classifications of Application Control Policies incident types to provide granularity and rapid triage of the incident.
Operational Efficiencies - Flexible Software Deployment Models
Day 2 operations require flexible deployment options to integrate within an IT organization’s processes and best practices. In previous releases, customers needed to bring an entire server group into maintenance mode when updating a server workload.
IT Operations teams can now deploy, upgrade or maintain Virsec probes on a per-host/server basis. These capabilities are available through the management console as well as APIs for deeper integration into your change management process. This new capability provides much more flexibility for teams to manage servers independently, ensuring the production environment's stability and resilience.
See Virsec's Allowlisting Using Maintenance Mode ![]()
Ease of Use - Guided Deployments
The Virsec Security Platform (VSP) now offers an easy guided deployment option for Virsec Probes. Deployment Profiles now output the required commands for Probe installation based on the user-selected options. It drastically reduces the opportunity for user entry errors and user dependency on product documentation. 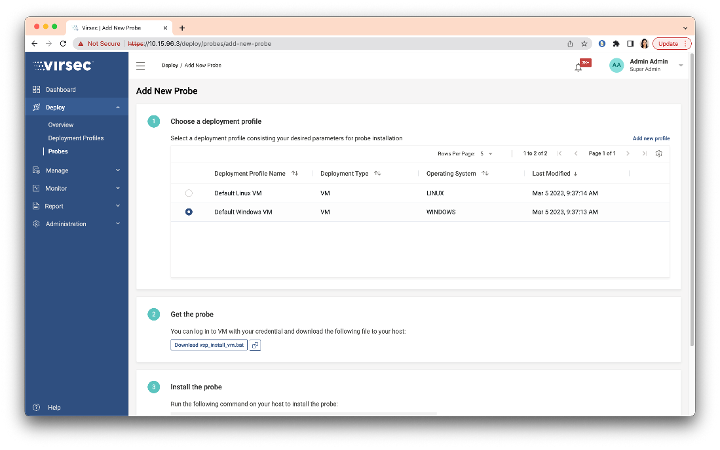
Virsec Probe Deployment – Guided Journey
See Virsec's Guided Probe Deployment ![]()
Summary
Extending Zero-Trust Protection principles to applications workloads is critical for IT organizations to secure their data and server assets. As Verizon’s Breach Report highlights, 80% of breaches occur on servers. Servers and their application workloads present a high-value target rich with data, user profiles, and potential lateral movement to other assets; protecting these server workloads with Zero Trust Protection principles such as ‘deny all’ and ‘guilty until proven innocent’ are critical to proactively securing your digital environments.
Read the press release here.
For further information on Virsec’s approach to extending Zero Trust to application workloads and VSP 2.7 specifically, please visit www.virsec.com.